U.S. Pharmacy Market 2030: Future-Proofing Independent Pharmacies
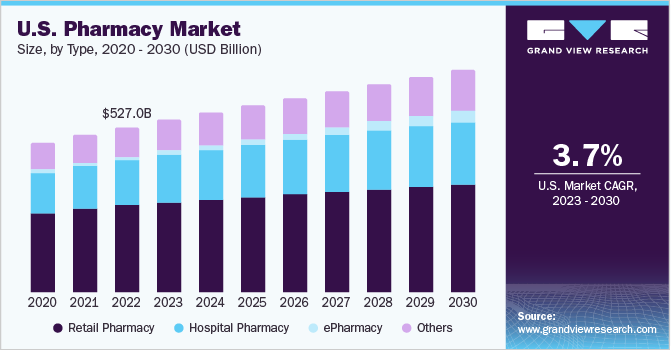
The U.S. pharmacy market size is projected to reach an impressive USD 708.9 billion, underscoring the immense potential and ongoing transformation within this vital industry.
The Digital Pharmacy Shift: Kiosks, Telepharmacy, and E-Commerce in the U.S. Market
Remember the days of long pharmacy lines and limited hours? For industry professionals, it is clear: the traditional pharmacy model is rapidly evolving. The future of medication access in the U.S. looks dramatically different, driven by technological innovations that are reshaping how patients interact with pharmaceutical services. This transformation is not just about convenience but about optimizing efficiency, expanding reach, and fundamentally enhancing the patient experience. This article explores the current trends and future outlook for pharmacy kiosks and telepharmacy, along with the growing role of e-commerce and home delivery services in the pharmacy sector. As we look towards 2030, the U.S. pharmacy market size is projected to reach an impressive USD 708.9 billion, underscoring the immense potential and ongoing transformation within this vital industry.
Pharmacy Kiosks and Telepharmacy: Expanding Access Through TechnologyPharmacy kiosks are self-service, automated machines designed to provide around-the-clock access to prescription and over-the-counter medications. These kiosks have become increasingly common in airports, clinics, rural areas, and university campuses. Many units feature touchscreen interfaces and remote communication capabilities, enabling real-time consultations with licensed pharmacists.
Increased Accessibility: Kiosks offer convenient access to medications in locations where full-service pharmacies may be unavailable, especially in rural or underserved communities.
Time Efficiency: These machines provide quicker service for routine prescriptions, often completing transactions in minutes.
24/7 Availability: Kiosks are operational beyond typical pharmacy hours, enhancing flexibility for patients.
Connected to cloud-based systems, pharmacy kiosks are typically supported by licensed telepharmacists who oversee prescription validation and patient counseling. This integration ensures compliance with regulatory standards while extending pharmacy services beyond traditional physical settings.
Growth of Telepharmacy ServicesTelepharmacy involves the use of digital communication technologies to deliver pharmacy services remotely. These services include prescription verification, medication counseling, and drug utilization reviews, all conducted by licensed pharmacists located off-site.
As stated by National Institutes of Health, despite its global success, strong support from pharmacy organizations, and proven safety in medication dispensing and adherence, telepharmacy faces significant policy hurdles in the U.S. While 28 states permit its use, varying and often burdensome regulations hinder its broader adoption, limiting its potential to expand access and improve patient care.
Telepharmacy offers a scalable solution that addresses staffing challenges while maintaining patient safety and quality standards. As technology continues to evolve, telepharmacy is expected to become a core component of pharmacy operations in both rural and urban markets.
E-Commerce and Home Delivery: Meeting Consumer ExpectationsThe expansion of e-commerce in the pharmacy sector reflects a broader consumer shift toward digital convenience. Patients increasingly prefer to order medications online and receive them at home, mirroring expectations shaped by retail and grocery delivery services.
While large players such as Amazon Pharmacy have entered the space, local and independent pharmacies are also adopting online platforms and delivery models to remain competitive.
Key Developments in Pharmacy E-CommerceOnline Refill Portals: Many pharmacies now offer secure websites and mobile applications where patients can request refills, view prescription history, and receive notifications.
Local Delivery Integration: Pharmacies are partnering with delivery services such as DoorDash, Uber Health, and regional couriers to offer same-day delivery for prescriptions and health products.
Subscription Models: Monthly medication delivery plans with built-in refill management and customized packaging are gaining popularity, particularly for chronic care patients.
This transition to digital services allows pharmacies to streamline operations and improve patient adherence. It also presents new opportunities to expand product offerings, such as vitamins, wellness items, and durable medical equipment.
Industry Implications and Operational ConsiderationsThe adoption of kiosks, telepharmacy, and e-commerce brings several strategic benefits but also introduces operational challenges that must be addressed.
- Regulatory Compliance
Telepharmacy and automated dispensing systems are subject to state-specific regulations. Ensuring compliance with federal and state laws, including those related to prescription verification, licensure, and privacy, is essential for continued adoption.
- Data Security
As patient data is processed through various digital platforms, pharmacies must implement robust cybersecurity measures and maintain full compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- Patient Education
Not all patients are familiar with kiosk technology, mobile applications, or video consultations. Pharmacies must invest in clear communication and training resources to support patient engagement with these new services.
- Outlook for the Future
Pharmacy kiosks, telepharmacy solutions, and e-commerce platforms represent a shift toward more accessible, flexible, and technology-driven care. These tools extend the reach of pharmacy services, reduce wait times, and offer new revenue streams for independent operators and chain pharmacies alike.
The pharmacy sector is undergoing rapid digital integration, driven by technological innovation, policy changes, and evolving patient expectations. Continued investment in infrastructure, workforce training, and regulatory alignment will be necessary to fully realize the potential of this transformation.
The next phase of pharmacy services in the U.S. will likely focus on hybrid models that combine digital access with personalized care, meeting patients where they are while maintaining clinical excellence.
Conclusion As consumer behavior continues to evolve and healthcare becomes more digitized, the U.S. pharmacy industry is well-positioned to deliver greater access and convenience through innovations in kiosks, telepharmacy, and online services. These advancements represent not just a shift in how pharmacy services are delivered, but a broader evolution in how healthcare is experienced.