Cross Border Payments Market 2030: Regional Trends Shaping the Industry
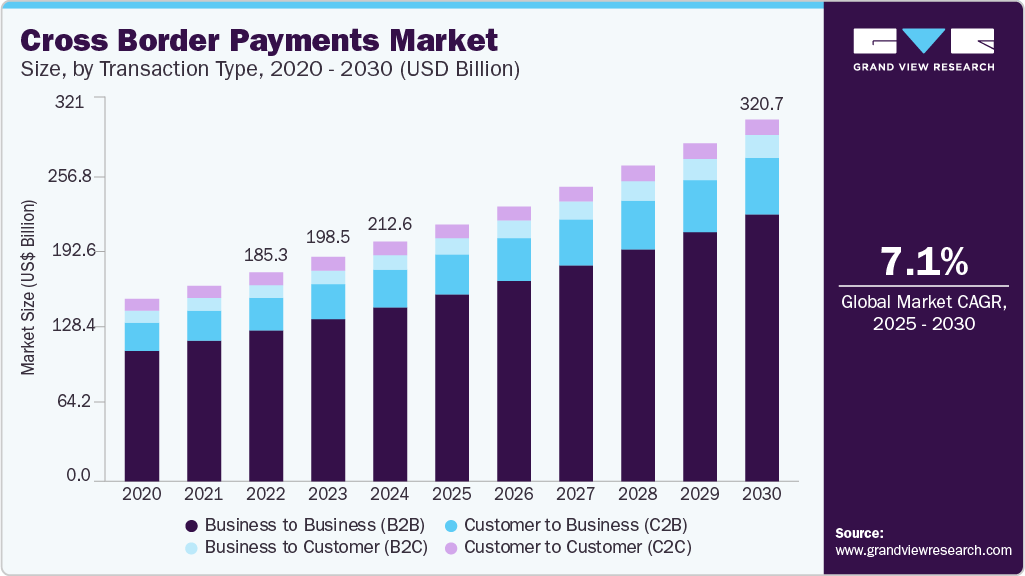
The global cross-border payments market was valued at USD 212.55 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 320.73 billion by 2030.
The global cross-border payments market was valued at USD 212.55 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 320.73 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 7.1% from 2025 to 2030. Despite growing volumes, cross-border payments remain costly and slow, prompting calls for reform.
According to the World Bank, the average cost of sending USD 200 in 2023 ranged between 6.2% and 6.3%, significantly exceeding the 3% target set under the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Regional disparities persist: remittance fees to South Asia averaged 6–7%, while transfers into Africa often exceeded 7%. These inefficiencies stem from layered correspondent banking processes and manual compliance checks.
In response, global efforts led by the G20 and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) have focused on enhancing cross-border payments to be “faster, cheaper, more transparent, and more inclusive.” Central banks are increasingly analyzing cost structures in specific corridors, such as Turkey to Bulgaria, where fees exceed 50%, and tracking progress on the G20 Roadmap. Organizations like the IMF and FSB have placed significant emphasis on reducing the cost of remittances and trade-related payments.
To address these challenges, industry stakeholders are upgrading infrastructure. The global rollout of the ISO 20022 messaging standard is accelerating. For instance, the UK’s CHAPS system completed its ISO 20022 migration in 2023, with the Bank of England aiming to align with BIS/CPMI data requirements by 2025. Uniform data formats improve automation and reduce delays in cross-border transactions.
Another key modernization area is real-time payment connectivity. Today, more than 70 national Fast Payment Systems (FPS) operate worldwide. Linking these systems across borders is increasingly viewed as essential to achieving near-instant, low-cost international transfers. Thus, enhancements in payment rails—such as ISO 20022 adoption and FPS/RTGS interlinking—are driving industry growth, supported by active engagement from central banks and global regulators.
Order a free sample PDF of the Cross Border Payments Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
Key Market Trends & Insights
- North America held a 27.8% share of the global cross-border payments market in 2024. Modernization initiatives, including the FedNow Service in the U.S., are aimed at improving efficiency and reducing costs in cross-border transactions.
- The Business-to-Business (B2B) segment dominated transaction types with a 72.6% market share in 2024. Multinational corporations conduct most of these transactions via global treasury systems and SWIFT, driven by international trade and supply-chain needs.
- Bank transfers accounted for the largest share by payment channel in 2024. Traditional banking infrastructure—especially SWIFT-based wire transfers—remains central for high-value transactions. However, modernization efforts like SWIFT GPI now allow banks to offer real-time tracking of cross-border payments.
- Large enterprises led the market by enterprise size in 2024. These firms benefit from advanced treasury platforms, multi-currency accounts, and integration with ERP systems, which allow for optimized cross-border liquidity management.
- The business segment dominated end-use categories in 2024 and is expected to grow significantly. This includes B2B transactions, cross-border e-commerce, and intercompany transfers. Even for SMEs, the underlying infrastructure is often similar to that used in larger corporate transactions.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 212.55 Billion
- 2030 Projected Market Size: USD 320.73 Billion
- CAGR (2025-2030): 7.1%
- North America: Largest market in 2024
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
The global cross-border payments landscape is dominated by a few major players, including PayPal, Western Union, Wise Payments Limited, MoneyGram, Visa, and Mastercard. Their large customer bases, established networks, and regulatory experience position them as leaders in this space. They offer diverse solutions—ranging from digital wallets and real-time transfers to corporate treasury services.
- PayPal: A global leader in digital payments, offering services for individuals and enterprises. Its remittance platform, Xoom, began using PayPal USD (a stablecoin) in 2024 to improve remittance speeds. PayPal’s broad portfolio includes multi-currency wallets, global e-commerce payments, and enterprise solutions like PayPal Complete Payments, recently launched in China.
- Wise Payments Limited: A fintech specializing in low-cost, transparent international transfers and multi-currency accounts. Wise charges 0.5–1% fees and settles payments directly in local currencies. In 2024, it gained direct access to Japan’s Zengin clearing system, and launched in Mexico in early 2025, expanding into key remittance corridors. The company reported USD 185.2 billion in cross-border volume in FY2025 and is targeting double-digit margins by 2026.
Key Players
- PayPal
- Western Union Holdings
- Wise Payments Limited
- MoneyGram
- Visa
- Mastercard
- Stripe, Inc.
- Payoneer Inc.
- Worldpay LLC
- Airwallex
- Rapyd Financial Network Ltd.
Explore Horizon Databook – The world's most expansive market intelligence platform developed by Grand View Research.
Conclusion
The cross-border payments industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by cost and speed pressures, regulatory mandates, and technological innovation. Although inefficiencies like high remittance fees persist—especially in developing regions—the market is steadily moving towards real-time, low-cost, and transparent solutions.
The adoption of standardized messaging (ISO 20022), real-time payment infrastructure, and digital innovation by leading players are reshaping the global landscape. As central banks and international institutions push reforms, and private players innovate with digital currencies, APIs, and network expansion, the industry is well-positioned for sustained growth. By 2030, with an expected market value of USD 320.73 billion, cross-border payments will likely be faster, cheaper, and more integrated than ever before.